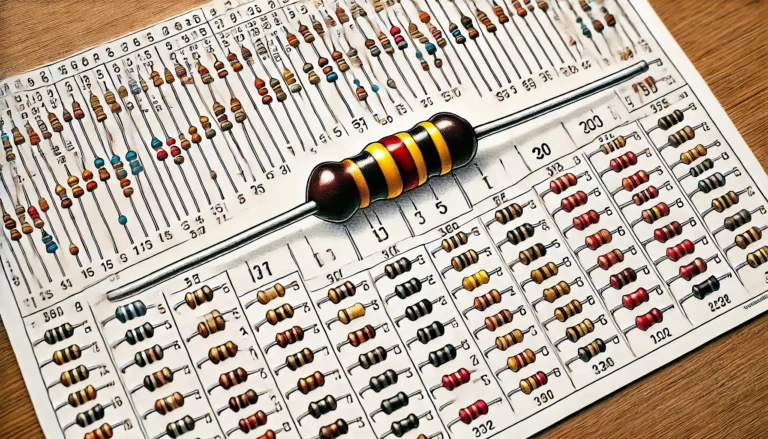
4 Band Resistor Color Code
Four-band resistors—oh, how they weave their magic in the realm of electronics! Renowned for their reliability and precision, these little heroes play pivotal roles in myriad components. Take voltage dividers, for instance; they’re like skilled artisans, deftly reducing voltage levels to suit specific needs with finesse. But that’s just scratching the surface!
These resistors step up as guardians in current limiting applications too, shielding delicate components such as LEDs from an onslaught of excess current that threatens to wreak havoc and cause untimely damage. Can you feel the tension? It’s palpable.
And there’s more! When we dive into filter circuits, 4-band resistors shine yet again. They’re not merely passive players; they sculpt frequency responses with a craftsman’s touch—allowing select frequencies to pass through while mercilessly attenuating others like gatekeepers at an exclusive club. Their knack for providing both stability and unwavering performance makes them indispensable allies in the world of analog devices, ensuring everything runs smoothly across diverse electronic systems. What a fascinating dance of technology they perform!
Usage in Electronic Circuits
Ah, resistors—the unsung heroes of electronic circuits—wielding their mighty influence over the currents that pulse through our devices! They don’t just sit idly by; oh no! These little champions regulate current flow with finesse, shielding delicate components from the looming specter of damage. Picture this: they deftly set voltage levels, divide voltages like a skilled magician slicing a rope, and tame currents to fit the whims and needs of various circuit inhabitants.
Imagine their myriad applications—a biasing partner for transistors in amplifiers, a steadfast creator of reference voltages for operational amplifiers, or even as load resistance for sensors embarking on their data-collecting journeys. The artful selection of resistor values? Absolutely paramount! It’s not merely an exercise in choice but rather a dance that ensures optimal functionality and unwavering reliability across diverse circuit designs.
But wait, there’s more! Resistors also step into the limelight in communication systems where they perform signal attenuation and conditioning with aplomb. Think about audio equipment—they swoop in to alleviate impedance complications and ward off distortion like guardians at the gates. And let us not forget their essential role in timing circuits alongside digital logic designs—forming intricate RC (resistor-capacitor) networks that orchestrate precise timing intervals.
The adaptability of these resistive wonders is nothing short of remarkable! Engineers wield them like Swiss Army knives within an array of electronic applications, enhancing performance while boosting efficiency at every turn. Truly, what would our circuits be without these stalwart allies?
| Resistor Type | Common Application | Power Rating (W) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Film Resistor | General purpose in electronic circuits | 0.25 – 2 |
| Metal Film Resistor | Precision applications in amplifiers | 0.125 – 1 |
| Wirewound Resistor | High-power applications like automotive | 1 – 100 |
| Variable Resistor (Potentiometer) | Volume controls in audio devices | 0.1 – 2 |
| Surface Mount Resistor | Compact circuits in modern electronics | 0.05 – 0.5 |
Differences Between 4 Band and 5 Band Resistors
Four-band resistors and five-band resistors—two cousins in the vast realm of electronic circuits—share a common mission, yet they dance to different tunes when it comes to precision and the wealth of information they convey. Picture this: the four-band resistor strutting its stuff with a significant figure, followed by a multiplier and an elegant tolerance. It’s like the dependable workhorse of circuitry, perfect for everyday tasks where general applications reign supreme.
Now, enter stage left—the five-band resistor! This little marvel takes things up a notch by adding an extra significant figure into the mix. Can you feel that? A surge in precision that’s not just impressive but downright essential for specialized scenarios where every ohm counts towards circuit performance. The magic lies in that additional band, often acting as a third significant digit; it broadens the spectrum of resistance values like never before.
Thus, five-band resistors become champions in environments demanding tighter tolerances—think precision amplifiers or those sensitive measurement devices that can’t afford even the slightest hiccup. While four-bands hold their ground as reliable stalwarts for standard tasks, it’s clear: when accuracy is non-negotiable and performance is king, five-band resistors take center stage without breaking a sweat.
Understanding Additional Band Functions
In the intricate world of resistors, an additional band in a 5-band design emerges not merely as an ornament but as a pivotal element—enhancing the precision of resistance measurement to new heights. This extra band typically signifies either the tolerance or temperature coefficient, unraveling vital information about how this little component behaves when tossed into various conditions. Imagine a resistor with tighter tolerances—a beacon of reliability in high-stakes applications where even the slightest deviation can unleash significant consequences.
Now, let’s delve into the contrasting functionalities nestled within different band configurations. The 4-band design leans toward simplicity and effortless identification, its charm lying in straightforwardness. In both designs, oh-so-familiar color codes dance for the first three bands: they embody significant figures and multiplier magic while reserving that fourth band to confidentially whisper about tolerance levels. Grasping these nuances empowers engineers and technicians alike to handpick just the right resistor tailored to their unique needs—ultimately weaving together threads of efficiency in circuit performance that hums along harmoniously!
Troubleshooting Resistor Issues
Diving into the labyrinth of resistor dilemmas demands a meticulous strategy, one that unravels the intricate faults potentially lurking beneath the surface, threatening circuit integrity. Picture this: armed with a digital multimeter—a precision instrument that transforms ambiguity into clarity—you embark on a quest for resistance measurements. The beauty of this tool lies in its ability to deliver exact readings, setting them side by side against those specified values like two rivals staring each other down. A stark divergence? Ah, therein lies the whisper of trouble, perhaps hinting at scorching damage or sneaky short circuits.
Now, should you find yourself suspecting an errant or weary resistor—perhaps one that’s seen better days—the next logical step is crystal clear: swap it out for one that matches perfectly in type and rating. This isn’t just about restoration; it’s about reviving functionality with finesse! But wait—there’s more to ponder! Grasping how tolerance and power rating weave their influence across circuit dynamics paves the way for astute troubleshooting and ingenious remedies.
And let us not overlook another gem in your toolkit: keeping meticulous tabs on resistor values within your circuitry. It’s like having a treasure map when issues rear their heads—guiding you toward which components deserve your immediate attention first! Armed with appropriate tools and an organized approach—not only will you streamline your troubleshooting journey—but you’ll also bolster the reliability of your electronic endeavors as they pulse back to life!
Identifying Faulty Resistors
Faulty resistors—oh, the havoc they can wreak on electronic devices! The performance of these gadgets hinges precariously on the integrity of their components. To unearth such issues, one must don a detective’s hat, employing both keen visual inspections and astute testing methods. Picture this: telltale signs of a defective resistor might leap out at you—burns or discoloration marking its surface like battle scars. Such indicators often hint at overheating or an unwelcome surge in current flow, paving the way to circuit calamity.
Now, armed with a trusty multimeter, you embark on your quest for truth—the resistance values will reveal all! A reading that strays from the prescribed range? That’s your red flag waving furiously—a problem lurks beneath!
But wait! There’s more to this puzzle than mere numbers. Consider how each resistor dances within the grand ballet of the circuit itself. If things aren’t performing as they should—a cacophony instead of harmony—it may be time to suspect resistor failure is casting shadows over your project. In circuits brimming with complexity and multiple components, isolating that pesky resistor for individual scrutiny becomes paramount; it reveals secrets hidden in plain sight.
And let us not forget our ally—the circuit diagram! This map can illuminate whether your resistor is fulfilling its role or simply coasting along aimlessly. Tread carefully through troubleshooting; methodical steps are essential to prevent further damage and cut down on precious time spent unraveling these tangled webs of electronics!
- Inspect resistors for visible signs of damage such as burns, cracks, or discoloration.
- Use a multimeter to measure resistance values and compare them against the specified ratings.
- Isolate resistors from the circuit for individual testing to determine if they are functioning properly.
- Cross-reference findings with the circuit diagram to ensure each resistor is correctly placed and used.
- Document all measurements and observations to track changes and identify patterns over time.
- Consider environmental factors that may contribute to resistor failure, such as excessive heat or moisture.
- Evaluate the overall performance of the circuit to help pinpoint issues that may be related to faulty resistors.
Best Practices for Resistor Selection
When diving into the world of resistors, one must navigate a maze of considerations—chief among them, the resistance value and tolerance. The resistance value acts as a gatekeeper, dictating how much current will dance through the circuit’s veins. Meanwhile, tolerance whispers secrets about permissible deviations from that value—a crucial detail for those seeking precision in their endeavors. For applications where accuracy reigns supreme, opting for a resistor with lower tolerance becomes imperative; it’s the key to unlocking optimal performance.
But wait! There’s more lurking beneath the surface: power rating looms large on this stage too. Ignoring it could spell disaster—overheating and catastrophic failure lurk around every corner in high-power circuits if you’re not careful.
Now let’s pivot our gaze towards environmental factors—they play a pivotal role in your selection process. Operating temperature range? Absolutely essential! Some materials might crumble or alter their resistance when subjected to extreme conditions like an unyielding summer sun or frigid winter chill. And don’t forget moisture sensitivity! In humid settings, certain resistor types may fall prey to corrosion or even outright fail—the horror!
Lastly, we can’t overlook size and configuration; they’re not mere trifles but rather vital elements that demand attention to ensure compatibility with your circuit layout’s design requirements. Prioritizing these multifaceted factors leads you down the path toward crafting circuits that are not just functional but also reliable and efficient—an engineer’s dream come true!
Factors to Consider Before Purchasing
When diving into the world of resistors, one must think carefully about that elusive resistance value. Oh, how it can dramatically sway the performance of any circuit housing this humble component! But wait—tolerance also rears its head as a crucial player in this game. It’s all about how closely the actual resistance aligns with what’s promised on the label. A lower tolerance percentage? That’s your golden ticket to precision—a must-have for those delicate electronic applications where every minuscule deviation could spell disaster.
And let’s not forget power rating—it’s like the resistor’s stamina badge, revealing just how much juice it can tolerate without succumbing to thermal demise. This aspect gains even more gravity when you’re dealing with high-power scenarios; excess heat is an enemy lurking around every corner, threatening to scorch and ruin precious components. Plus, we can’t ignore the environmental elements at play: temperature fluctuations and humidity levels may seem trivial but wield significant influence over a resistor’s lifespan and dependability across various operating landscapes. So choose wisely!
Resources for Further Learning
For those eager to unravel the intricate tapestry of resistor color codes and their myriad applications, a treasure trove of resources awaits. Consider diving into the pages of “The Art of Electronics” by Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill—this tome is not just foundational; it traverses the landscape from novice to seasoned expert with ease. Yet, that’s merely scratching the surface! The vast expanse of technical websites and online forums bursts forth with insights galore, tackling everything from rudimentary electronics to the labyrinthine intricacies of complex circuit design.
But wait! There’s more! Online courses and video tutorials emerge as invaluable companions for those who thrive on visual learning. Platforms like Coursera and Udemy are often brimming with comprehensive offerings that delve deep into electronic principles, complete with in-depth explorations on resistors themselves. And let’s not forget about community hubs like Stack Exchange—these vibrant spaces ignite knowledge-sharing and collaborative problem-solving among fellow enthusiasts, transforming what could be a solitary journey into an engaging exchange that demystifies queries relating to resistor color coding and beyond.
Recommended Books and Websites
For those on a quest to unravel the mysteries of resistor color codes and their myriad applications, an array of resources awaits your exploration. “The Art of Electronics” by Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill stands tall in the pantheon of electronic literature, revered for its exhaustive dive into components like resistors. This tome melds practical insights with theoretical wisdom, rendering it an essential companion for novices and seasoned engineers alike—think of it as a treasure trove brimming with knowledge.
But wait! The digital realm expands your horizons even further. Websites such as Electronics Tutorial burst forth with interactive tools and guides that demystify the often-confounding color coding process. It’s like having a trusty guide through a labyrinthine world where colors hold secrets.
Furthermore, don’t overlook reputable sites like SparkFun and Digi-Key—they’re goldmines teeming with detailed articles and how-to manuals. Each platform boasts dedicated sections on resistor selection and electronic circuit design, serving up not just technical know-how but also ensuring that you wield resistors accurately and efficiently across diverse projects.
Delving into these literary gems and engaging online content does more than just boost one’s technical prowess; it fortifies understanding while nurturing a more adept approach to assembling electronics or tackling troubleshooting conundrums. So gear up, because this journey promises both enlightenment and empowerment in the electrifying world of circuits!
Conclusion
Diving into the labyrinthine world of 4 band resistors is a must for anyone dabbling in the realm of electronic circuits. These little components, with their vast array of uses—ranging from the simplest gadgets to intricate systems—underscore their pivotal role in today’s tech landscape. The distinctions between 4 band and 5 band resistors unveil layers of advanced functionality tailored for specific requirements, bestowing designers with a rich palette of options when it comes to circuit schematics and layouts.
Navigating the waters of proper selection and troubleshooting methods is paramount; it ensures that projects not only function but thrive. By adopting smart practices in choosing resistors—including grappling with resistance values and tolerances—you can significantly boost your electronic applications’ performance. A commitment to ongoing learning in this field arms individuals with essential tools, enabling them to tackle challenges head-on while fine-tuning their circuit designs with finesse.