How to Decode Resistor Color Bands
Table Of Contents
How to Decode Resistor Color Bands and Understand Resistor Color Code and Band Colors
Key Takeaways
- Grasping Resistor Hue Patterns
- Interpreting Resistor Color Stripes
- Recognizing 4-Band Resistor Shades
- Investigating 5-Band Resistor Hues
- Familiar Colors and Their Corresponding Values
- Real-World Uses of Resistor Color Patterns
Understanding Resistor Color Codes
Resistor color codes serve as a universal language for identifying the values and tolerances of resistors. Each color represents a specific digit or multiplier, making it essential to understand how to decode resistor color bands accurately. By familiarizing oneself with the resistor color code, individuals can easily determine the resistance value of standard resistors, including the less common zero-ohm resistor. Mastering this decoding process ensures efficient circuit design and troubleshooting, allowing for precise electrical applications and enhanced performance. Knowing how to decode resistor color bands empowers both novice and expert electricians to work effectively with various resistive components.
What Are Resistor Color Codes?
Resistor color codes serve as a universal language that conveys the resistance value of resistors through a series of colored bands. These bands represent specific numerical values and tolerances, allowing individuals to determine the resistance without the need for measurement tools. Understanding how to decode resistor color bands is essential for anyone working with electronic components, as it ensures the correct application of resistors in circuits. Such codes are also relevant for identifying components like zero-ohm resistors and carbon-composition resistors, which have their own unique marking systems.
The color code system is not limited to resistors; it also applies to capacitors. Hence, recognizing the marking codes for resistors and capacitors is vital in electronics. A common application of resistors includes their use as pull-down resistors, which stabilize the voltage levels in a circuit. Gaining proficiency in how to decode resistor color bands is important for troubleshooting and building circuits with precision. The effective use of this coding system enhances both the efficiency and safety of electronic projects.
Importance of Resistor Color Codes
Resistor color codes are essential for ensuring accurate resistance values in electronic components. Understanding how to decode resistor color bands allows technicians and hobbyists to identify the resistance of any resistor placed on a circuit board. The colors of the bands, such as red, green, and silver, signify specific values and tolerances, providing vital information for electronic design and troubleshooting. Grasping these concepts is crucial for functioning circuitry, especially when dealing with 4-band resistor color codes where precision is key.
Recognizing the significance of resistor band colors enhances one’s ability to work effectively with electronic devices. The correct interpretation of these colors affects the performance and reliability of electronic circuits. Knowing how to decode resistor color bands is not just helpful; it is fundamental for engineers and DIY enthusiasts alike. This knowledge enables them to select appropriate resistors, thereby optimizing their projects for efficiency and safety.
Decoding Resistor Color Bands
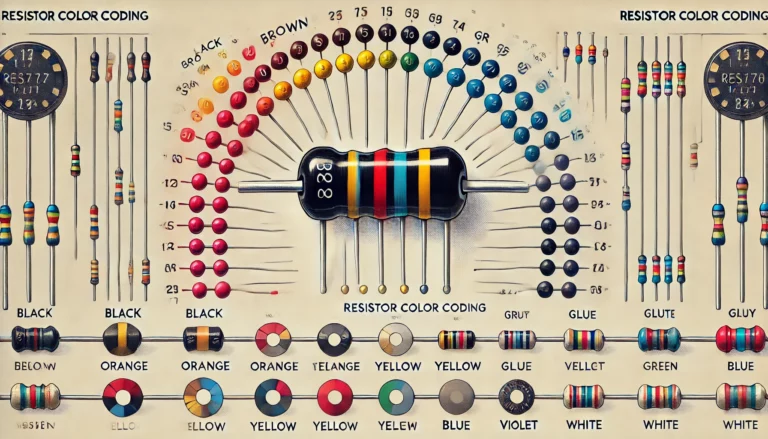
Understanding how to decode resistor color bands is essential for anyone working with electronic components. The process varies slightly between a 4-band resistor and a 5-band resistor, primarily due to the number of colors and their corresponding values. For a 4-band resistor, the first two bands represent significant digits, the third band indicates the multiplier, and the final band denotes tolerance. In contrast, the 5-band resistor adds an extra significant digit, allowing for more precise values which enhances the accuracy of the resistor color code. Familiarity with color code resistors requires a clear grasp of the color code associated with different values, ensuring effective decoding in various applications. Understanding these nuances equips one with the skills necessary to work confidently with different band type resistors.
- Familiarize yourself with the standard color code chart for resistors.
- Memorize the values assigned to each color to aid in quick identification.
- Practice decoding various resistors to improve speed and accuracy.
- Be aware of the common tolerance values associated with different colors.
- Understand the differences in resistance values between the four-band and five-band configurations.
- Use a multimeter to verify resistance values when in doubt.
- Keep a color code reference card handy for easy access while working on projects.
How to Decode Resistor Color Bands
Decoding resistor color bands involves understanding the significance of each colored band on the resistor. For a four-band resistor, the first two bands represent significant digits, the third band indicates a multiplier, and the fourth band signifies tolerance. In five-band resistors, the procedure adds an extra significant digit, making it essential to recognize the additional color band. Six-band resistors include even more information, commonly adding a temperature coefficient band. Knowing how to decode these bands is crucial for accurately understanding resistor values.
To effectively decode the color bands, you’ll need a color code chart that matches the colors to their respective values. Each band has a specific meaning and represents a numerical value, helping to calculate the resistance. This process is similar for three-band resistors, where the color bands denote a more basic resistor value. Mastering how to decode resistor color bands requires practice, especially when distinguishing between the different types of band resistors like five-band and six-band resistors, each with its unique structure.
Tools Needed for Decoding
Understanding how to decode resistor color bands requires a few essential tools. A color code chart is invaluable, providing quick reference for identifying the resistor values for both four-band resistors and five-band resistors. A multimeter can help confirm the resistor values, making it easier to verify your findings. A popular resistor kit can also be beneficial, as it contains various resistors, allowing you to practice decoding. Familiarizing yourself with a band resistor example can enhance your skills in interpreting these color codes effectively.
Having the right tools is crucial for precise and efficient decoding. A magnifying glass can aid in inspecting small color bands on new resistors, ensuring that you don’t miss any details. A printed reference guide that includes common color codes will serve as a helpful reminder during your decoding sessions. Practicing how to decode resistor color bands using these tools can lead to mastering the identification of resistor values, ensuring that you can work confidently with resistors in various electronic projects.
Identifying 4Band Resistor Color
Understanding the identification of 4-band resistors is crucial for anyone working with electronics. The basic structure consists of four color bands that indicate the resistor’s value and tolerance. Knowing how to decode resistor color bands allows for quick interpretation of these values. Typically, the first two bands represent significant digits, while the third indicates the multiplier, and the fourth denotes tolerance. For surface-mount devices (SMD resistors), the resistor illustration change is essential, as their compact format can complicate identification. Recognizing these band color codes accurately ensures that you can select the right resistor package for your project, preventing resistor changes that could affect circuit performance.
Basic Structure of a 4Band Resistor
The basic structure of a 4-band resistor consists of four colored bands that indicate its resistance value and tolerance. Each color corresponds to a specific number or multiplier. Understanding how to read resistors is essential for anyone working with resistor technology. Many resistors, including carbon-composition resistors and high precision resistors, utilize this color coding system. Knowing how to decode resistor color bands allows technicians and engineers to select the appropriate resistor for their circuits.
These resistors generally feature a cylindrical shape with bands painted around their body. The first two bands denote significant figures of the resistor value, while the third band represents the multiplier. The fourth band indicates the tolerance level, which is crucial for applications requiring specialized resistors. For example, an ohm resistor’s accuracy can greatly impact the functionality of an electronic device, making it vital to correctly read resistor color codes.
Reading 4Band Resistor Color Codes
Understanding how to read 4-band resistor color codes is crucial for effective circuit design and assembly. The first two colored bands indicate significant digits, while the third band represents the multiplier. It’s essential to recognize how to decode resistor color bands to ensure proper component usage. If an extra color band is present, it may signal tolerance or reliability, particularly in high-voltage resistors. This adjustment can impact the overall circuit functionality and the resistor’s derating affects under specific conditions.
Reading and interpreting these color codes accurately guarantees that you select the appropriate resistance values for your projects. The integration of the 5-band color system allows for more precision in higher resistance ranges, but many applications still utilize the reliable resistor structure of the 4-band system. Familiarity with colored bands enhances your capability to work effectively with diverse circuit elements. Engaging with the color codes opens doors to better understanding and implementing resistor specifications.
Exploring 5Band Resistor Color
Understanding 5-band resistors involves recognizing their complexity compared to 4-band resistors. Each band represents a specific value, with the first two colors indicating significant digits, the third band serving as a multiplier, the fourth band reflecting tolerance, and the optional fifth band often denoting temperature coefficient. The sixth band color may sometimes indicate special characteristics or functions, such as high voltage resistors or specific low resistance values. Knowing how to decode resistor color bands becomes essential for accurately interpreting these values. An automatic resistor calculator can simplify this decoding process, making it easier to work with different band colors and understand the overall color code system effectively.
Differences Between 4Band and 5Band Resistors
4-band and 5-band resistors serve distinct purposes in electronic circuits, particularly concerning precision and complexity. The 4-band resistor typically includes two color bands for significant digits, one for the multiplier, and a fourth band that denotes tolerance. Resistance values obtained from these units are straightforward to read, making them suitable for general applications. In contrast, the 5-band resistor introduces an additional color band that enhances accuracy. This additional band allows for a more precise measurement of resistance values, which is particularly beneficial for high-performance electronics.
Understanding how to decode resistor color bands becomes crucial for both types of resistors. A color code calculator can help identify the resistance values quickly. Common colors used in these bands range from red to brown, with silver bands indicating a higher tolerance level in 4-band versions. For 5-band resistors, the extra band often adds more detail to the measurements, which is essential for intricate circuit designs. By mastering how to decode resistor color bands, individuals can accurately determine the specifications of each resistor type.
Reading 5Band Resistor Color Codes
Understanding how to decode 5-band resistor color codes is crucial for accurate circuit design. Each color band corresponds to a specific number, with the first three bands representing significant figures of the resistance value. The fourth band indicates tolerance, while the fifth band, often a metallic band, provides additional precision. Technicians must be familiar with the specific colors, including gray bands that are significant in determining values. This process allows for a more precise actual resistance value compared to 4-band resistors.
Decoding 5-band resistors involves translating the colors of several bands into numerical values. The standard color code chart is essential for identifying each color’s corresponding digit. Each color plays a vital role in establishing the resistance value and its accuracy. Knowing how to decode resistor color bands effectively ensures that engineers and hobbyists can select the appropriate component for their electronic projects, enhancing the functionality of their designs.
| Color | Digit | Tolerance/Multiplier |
|---|---|---|
| Brown | 1 | ±1% |
| Red | 2 | ×100 |
| Green | 5 | ±0.5% |
| Blue | 4 | ×10^6 |
| Gray | 8 | ±0.1% |
Common Resistor Colors and Their Values
Understanding how to decode resistor color bands is essential for accurately determining resistor values. Each resistor’s colours provide critical information; for a 4-band type, the first two bands represent significant digits, the third color indicates the multiplier, and the fourth color denotes tolerance. For instance, a resistor with a first color of red, a second color of green, and a third color of brown translates to a value of 25 ohms with a tolerance indicated by the fourth band. Familiarity with these colors, including gold for tolerance, allows for quick and efficient identification of resistor values in various applications. The specific arrangement and meaning of these colors are crucial for anyone working with electronic components.
Overview of Common Resistor Color Options
Resistor color options are determined by a specific color code chart, which establishes the order in which colors represent numerical values. The most common band types include the black band, which corresponds to the value of zero, and the silver band, which indicates a tolerance of ±10%. Understanding how to decode resistor color bands is vital for accurately determining the resistance values and ensuring proper circuit functionality.
Different band types serve distinct purposes, such as identifying the resistor’s value, tolerance, and temperature coefficient band. Familiarity with the color order helps in deciphering the function of each band accurately. A simple glance at the color code chart will reveal the numerical significance of each color, paving the way for effective application in electronic projects. Knowing how to decode resistor color bands can significantly enhance problem-solving skills in electronic design.
Understanding Resistor Band Colors
Resistor band colors play a crucial role in determining the resistance values of these essential components. The actual bands on a resistor typically consist of three or four colored stripes that indicate the resistance value, tolerance, and temperature coefficient. The importance of the fourth band is particularly notable, as it usually represents the tolerance level of the resistor. Understanding how to decode resistor color bands helps in assessing circuit requirements accurately.
The arrangement of the bands varies based on the type of resistor being used. For instance, a gold band signifies a tolerance of 5%, while a silver band denotes 10%. Knowing how to decode resistor color bands not only simplifies the process of resistor selection but also ensures that the right components are integrated into electronic circuits. Each band’s color corresponds to a specific numerical value, allowing for precise calculations and reliable performance in various applications.
- Understanding the color code is essential for selecting the correct resistor for your project.
- The first two or three bands indicate significant digits, while the last band reveals the multiplier.
- Familiarize yourself with the color chart to quickly identify resistor values.
- For more precision, consider using digital multimeters to measure resistance directly.
- Always double-check values, especially in high-precision applications.
- Keep a color code reference handy for quick consultations when working on circuits.
- Practice decoding various resistor values to build confidence in component selection.
Practical Applications of Resistor Color Codes
Understanding how to decode resistor color bands is crucial for anyone working with electronic components. Resistor color codes serve as an essential guide that indicates the resistance value and tolerance of the resistors used in circuits. By interpreting the colors displayed on the resistor, one can accurately determine the specifications and ensure proper functionality in their projects. Knowledge of the resistor color code can also aid in identifying unique components, such as the zero-ohm resistor, which may not have traditional resistance values. Mastering this skill enables technicians and hobbyists alike to enhance their electronic designs effectively.
| Color | Digit Value | Tolerance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | N/A |
| Brown | 1 | 1 |
| Red | 2 | 2 |
| Orange | 3 | N/A |
| Yellow | 4 | N/A |
Conclusion
Understanding how to decode resistor color bands is essential for anyone working with electronics. The inclusion of an extra color band in a 5-band color system provides more precision, making it easier to identify reliable resistor values. This added complexity can influence how resistor derating affects performance, particularly in high-voltage applications. Familiarizing oneself with the various colored bands and corresponding color codes ensures accurate interpretation, which is crucial for maintaining circuit integrity. By mastering these decoding techniques, individuals can effectively work with both 4-band and 5-band resistors, enhancing their proficiency in electronics.
FAQS
How can I identify the resistance value of a 4-band resistor color code versus a 5-band resistor color code?
To identify the resistance value, first look at the color bands: a 4-band resistor color scheme includes two significant digits, a multiplier, and a tolerance band, while a 5-band resistor color adds a third significant digit, which increases accuracy. For instance, the fourth color band in a 4-band resistor indicates tolerance, while in a 5-band resistor, it enhances precision in basic resistor values. Additionally, a 6-band resistor may provide even more details, including more significant digits and additional tolerance bands; colors gold typically represent specific values and tolerances across different resistor types.
How do I identify the function of a pull down resistor in a circuit when comparing 6-band resistors versus resistors with a few bands?
A pull down resistor is used to ensure a particular color and voltage level in circuits, especially when involving resistor and capacitor configurations. When comparing 6-band resistors to those with fewer bands, it’s important to note that 6-band resistors provide more precision in resistance values, which can be crucial in complex circuits that require a top resistor for improved accuracy.
How do I distinguish between a resistor with few bands and a traditional multi-band resistor?
To distinguish between a resistor with few bands and a traditional multi-band resistor, you need to look closely at the number of color bands present. Resistors with few bands typically have less than four, while traditional multi-band resistors usually feature four or more bands that indicate their resistance value, tolerance, and sometimes temperature coefficient.
How can I accurately decode resistor color bands to determine their resistance values?
To accurately decode resistor color bands in order to determine their resistance values, refer to the color code chart that associates each color with a specific numeral. For example, the first two bands represent significant digits, the third band indicates the multiplier, and the fourth band may indicate tolerance. Always check if it’s a 4-band or 5-band resistor, as that will affect the calculation of the resistance value.
What techniques can I use to decode resistor color bands for identifying resistance values efficiently?
To decode resistor color bands efficiently, you can utilize techniques such as using a multimeter for direct measurement, applying the color code chart for deciphering values, and employing online calculators that simplify the process of determining resistance values based on color bands.