What Do Resistor Color Bands Mean
Resistors are a fundamental component in electronic circuits, playing a crucial role in controlling the flow of electric current. Understanding the color bands on resistors is essential for anyone involved in electronics, from hobbyists to professionals. In this article, we will delve into the meaning of resistor color bands, how to read them, and why they are important. By the end of this guide, you will have a clear understanding of how to decode resistor color bands and apply this knowledge in your projects.
The Basics of Resistor Color Bands
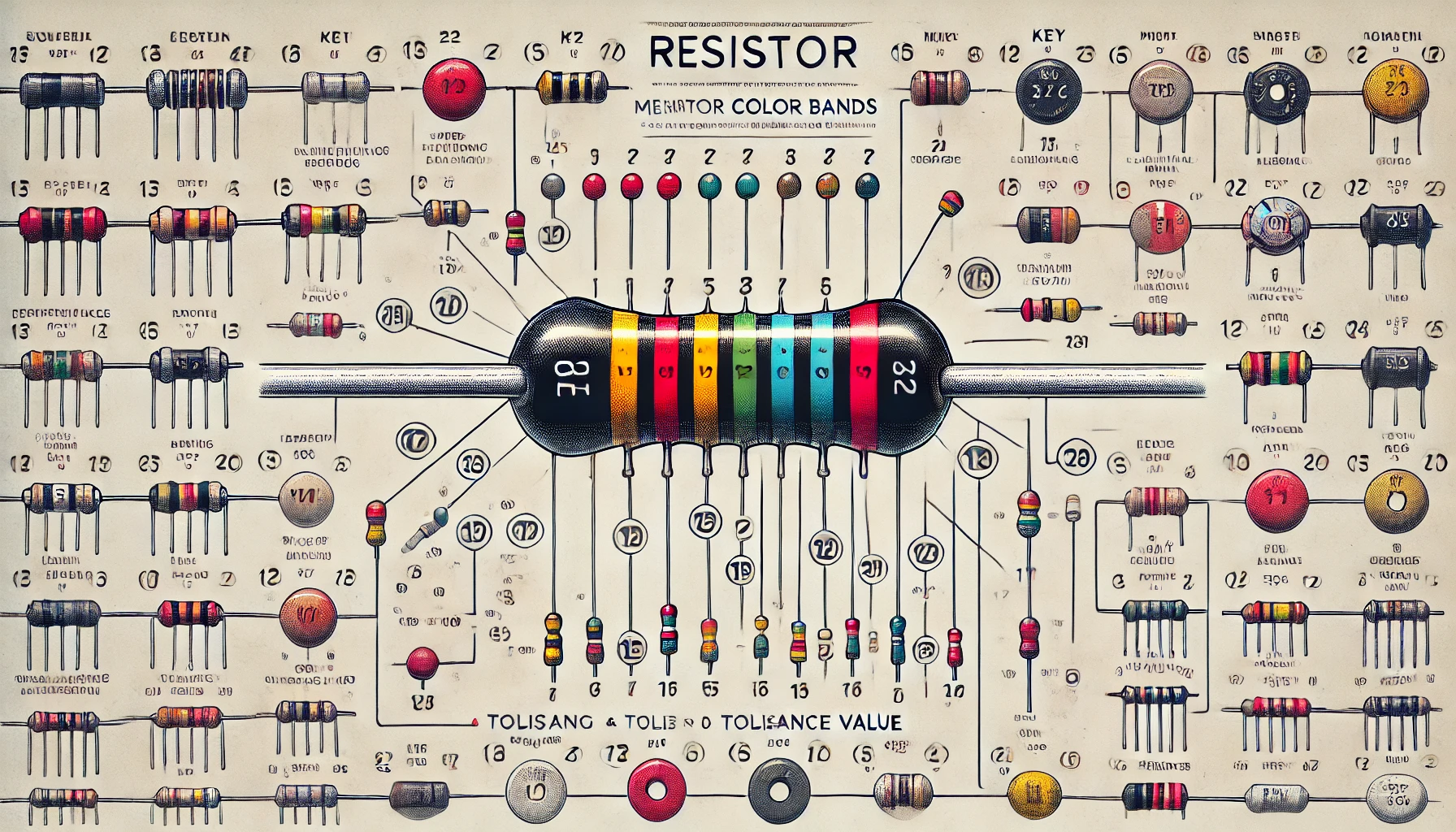
Resistor color bands are a system used to indicate the value of resistance and tolerance of resistors. Each resistor has a series of colored bands that represent numbers and multipliers. This system is standardized and widely used in the electronics industry.
Why Use Color Bands?
Color bands are used on resistors because they provide a simple and effective way to convey crucial information about the component. Unlike printed text, color bands are easy to read in various orientations and are resistant to wear and tear. This makes them ideal for small components where space is limited.
How to Read Resistor Color Bands
Reading resistor color bands involves understanding the color code and applying it to determine the resistor’s value. The resistor color code consists of several colors, each representing a specific number. Here’s a quick reference list of the color codes:
- Black: 0
- Brown: 1
- Red: 2
- Orange: 3
- Yellow: 4
- Green: 5
- Blue: 6
- Violet: 7
- Gray: 8
- White: 9
The Standard Resistor Color Code System
Typically, resistors have four, five, or six bands. Here’s how to interpret them:
Four-Band Resistors:
- The first band represents the first significant digit.
- The second band represents the second significant digit.
- The third band represents the multiplier.
- The fourth band indicates the tolerance.
Five-Band Resistors:
- The first band represents the first significant digit.
- The second band represents the second significant digit.
- The third band represents the third significant digit.
- The fourth band represents the multiplier.
- The fifth band indicates the tolerance.
Six-Band Resistors:
- The first band represents the first significant digit.
- The second band represents the second significant digit.
- The third band represents the third significant digit.
- The fourth band represents the multiplier.
- The fifth band indicates the tolerance.
- The sixth band indicates the temperature coefficient.
Example: Decoding a Resistor
Let’s decode a resistor with the following color bands: Red, Violet, Yellow, and Gold.
- Red (2) is the first digit.
- Violet (7) is the second digit.
- Yellow (4) means a multiplier of 10,000.
- Gold indicates a tolerance of ±5%.
So, the resistor value is 27 x 10,000 = 270,000 ohms (or 270k ohms) with a tolerance of ±5%.
Why Resistor Tolerance Matters
Tolerance is the percentage that indicates how much the actual resistance can vary from the stated value. For example, a resistor with a tolerance of ±5% can vary by 5% above or below the indicated resistance. Tolerance is crucial in precision circuits where exact resistance values are necessary for proper operation.
Practical Tips for Reading Resistor Color Bands
- Orient the Resistor Properly: Ensure you start reading from the correct end. The tolerance band is typically gold, silver, or clear and is usually separated slightly from the other bands.
- Use a Resistor Color Code Calculator: These calculators can quickly help you determine resistor values by selecting the colors of the bands.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Familiarity with the color codes will make reading resistors quicker and more accurate over time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Misreading Colors: Some colors can appear similar under poor lighting conditions. Ensure you have good lighting when reading resistor color bands.
- Ignoring the Tolerance Band: Always include the tolerance band in your calculations to understand the potential variation in resistance.
- Starting from the Wrong End: Double-check the orientation to ensure you start reading from the correct end.
Understanding resistor color bands is crucial for anyone involved in electronics. These color codes provide a quick and reliable way to determine the resistance and tolerance of resistors, which are vital components in electronic circuits. By mastering how to read these color bands, you can ensure that your electronic projects function correctly and efficiently. Whether you are a hobbyist or a professional, knowing how to decode resistor color bands is an essential skill that will enhance your electronics expertise. Keywords: resistor color bands, electronics, resistance, tolerance, electronic projects.
Conclusion
Resistor color bands are a fundamental part of electronics, providing a clear and effective way to indicate the value and tolerance of resistors. By understanding the color code system and how to apply it, you can accurately determine the specifications of resistors and ensure your electronic circuits function as intended. Remember to practice reading resistor color bands, use helpful tools like color code calculators, and avoid common mistakes to become proficient in this essential skill. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced electronics enthusiast, mastering resistor color bands will undoubtedly enhance your capabilities in the field of electronics.
For more detailed guides and practical tips on electronics, be sure to visit our blog regularly and stay updated with the latest in electronic components and techniques.